The ever-increasing volume of data generated by businesses, consumers, and devices has made big data analytics a vital tool for organizations. Analyzing vast datasets enables businesses to derive meaningful insights that improve decision-making and operational efficiency. Big data analytics allows organizations to stay competitive by uncovering hidden patterns and trends, making it essential for driving innovation and growth.
What is Big Data Analytics?
Big data analytics refers to the process of examining large, diverse datasets to uncover valuable insights. These datasets can be structured, semi-structured, or unstructured and often come in various formats. The four primary characteristics of big data—volume, velocity, variety, and veracity—pose challenges in processing and analysis. However, modern technologies such as cloud computing, machine learning, and data warehouses have made it possible to analyze big data efficiently. Big data analytics involves data mining, predictive modeling, and machine learning to help businesses make data-driven decisions. This process is crucial for understanding customer behavior, optimizing operations, and predicting future trends.
How Does Big Data Analytics Work?
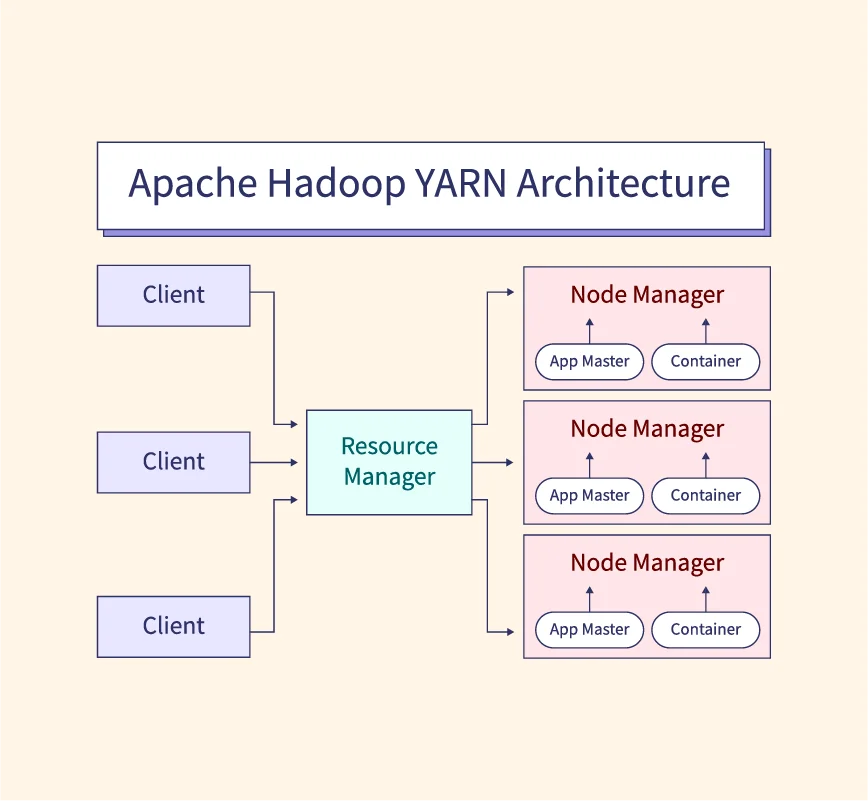
Big data analytics typically follows a multi-stage process that includes data collection, data processing, and data analysis. Initially, data is gathered from various sources such as customer interactions, social media, IoT devices, and transactional records. Once collected, the data is processed through tools like Hadoop, Apache Spark, and data warehouses, which organize and store the data for analysis. During the analysis phase, machine learning algorithms and statistical models are applied to extract meaningful insights. These tools enable organizations to derive predictions, identify patterns, and make informed decisions. Integrating AI and machine learning into big data analytics further enhances the ability to uncover deeper insights, driving better business outcomes.
The Importance of Big Data Analytics
Big data analytics has become a critical tool for organizations looking to maintain a competitive edge. By analyzing data in real-time, businesses can make faster, more informed decisions that improve operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. For instance, companies use big data analytics to monitor market trends, optimize supply chains, and personalize marketing efforts. It also plays a crucial role in risk management, helping businesses anticipate potential challenges and adapt accordingly. The ability to harness data for decision-making has transformed industries like healthcare, finance, retail, and manufacturing, enabling them to improve their processes and create more value.
Types of Big Data Analytics
Big data analytics can be categorized into four primary types:
- Descriptive
- Diagnostic
- Predictive
- Prescriptive
Each type serves a unique purpose in helping organizations derive insights from their data and make informed decisions.
1. Descriptive Analytics
Descriptive analytics focuses on understanding past data to identify trends, patterns, and insights. This type of analysis is often used to aggregate and summarize large datasets, helping businesses gain an overall understanding of their past performance. Techniques used in descriptive analytics include data summarization and visualization, where historical data is transformed into charts, graphs, and reports for easier interpretation. For example, businesses may use descriptive analytics to analyze sales reports, financial summaries, or website traffic to assess how they performed over a specific period. Descriptive analytics is foundational because it provides a baseline for more advanced types of analytics, allowing organizations to understand “what happened.”
2. Diagnostic Analytics
Diagnostic analytics goes one step further by analyzing past data to determine the underlying causes of certain outcomes. It helps organizations understand “why something happened” by employing techniques such as drill-down, data discovery, and correlation analysis. Diagnostic analytics is valuable for identifying the root causes of problems, such as why a particular product’s sales dropped or why a marketing campaign failed. For example, in manufacturing, diagnostic analytics can be used to conduct root cause analysis to determine why a machine malfunctioned. By pinpointing the factors behind specific outcomes, organizations can take corrective actions and improve their future performance.
3. Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics focuses on forecasting future outcomes based on historical data. By using statistical models, machine learning algorithms, and data mining techniques, predictive analytics helps businesses anticipate trends and make proactive decisions. For instance, companies in retail use predictive analytics to forecast sales patterns during different seasons, allowing them to adjust inventory and staffing accordingly. In finance, predictive analytics is employed for fraud detection, analyzing transaction data to identify suspicious patterns that could indicate fraud. This type of analytics empowers organizations to prepare for potential scenarios, reducing risks and optimizing outcomes.
4. Prescriptive Analytics
Prescriptive analytics goes beyond prediction to recommend specific actions that will help achieve desired outcomes. By using techniques such as optimization algorithms, simulation models, and decision trees, prescriptive analytics suggests the best course of action based on data-driven insights. For example, in supply chain management, prescriptive analytics can help optimize inventory levels and delivery schedules to minimize costs and maximize efficiency. Similarly, in dynamic pricing models, prescriptive analytics recommends price adjustments based on real-time data to increase profitability. This form of analytics is the most advanced and provides actionable recommendations for businesses to enhance their decision-making processes.
Conclusion
Big data analytics offers businesses the opportunity to gain a competitive advantage by deriving actionable insights from large datasets. By understanding the different types of analytics—descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive—organizations can make better decisions, improve operational efficiency, and enhance customer experiences. However, businesses must also navigate challenges such as data security, quality, and accessibility to unlock the full potential of big data analytics. As industries continue to evolve, the role of big data analytics will only grow, driving innovation and transforming the way organizations operate.
References: