The demand for data science professionals has skyrocketed as businesses increasingly rely on data-driven decision-making. From finance to healthcare, organizations leverage data to improve efficiency, optimize strategies, and gain a competitive edge.
This guide explores the diverse roles within the data science ecosystem, each serving a unique function in handling, analyzing, and interpreting data. Understanding these roles is crucial for aspiring data scientists, career switchers, and businesses looking to build strong data teams.
By the end of this article, you’ll gain a comprehensive understanding of various data science roles, their responsibilities, required skill sets, and career prospects. Whether you’re starting your journey in data science or looking to specialize, this guide will help you navigate the evolving landscape of data-driven careers.
Understanding the Data Science Job Landscape
The demand for data science professionals has surged due to the exponential growth of data and advancements in artificial intelligence. Businesses across industries rely on data-driven insights to make informed decisions, optimize processes, and enhance customer experiences.
Organizations typically structure data science teams based on their needs, combining various roles such as data scientists, analysts, engineers, and machine learning specialists. While some companies maintain dedicated data teams, others integrate data experts into different departments like marketing, finance, and operations.
Each data science role requires a unique blend of skills, including programming (Python, R, SQL), data visualization, statistical analysis, and machine learning expertise. Soft skills like problem-solving and communication are equally important for translating data insights into actionable business strategies.
Understanding these job roles is crucial for both professionals and businesses to effectively utilize data science in solving real-world challenges.
Top Data Science Roles and Their Responsibilities
Data science has emerged as one of the most promising fields, with diverse roles that enable organizations to unlock the potential of their data. From understanding patterns to predicting future trends, these professionals play a crucial role in transforming raw data into actionable insights. Here, we will explore the core data science roles, shedding light on the responsibilities, required skills, and industries that actively seek these professionals. This section will help you understand the varied career paths within the realm of data science, with a focus on how each contributes to organizational success.
1. Data Scientist
Data scientists are responsible for analyzing large datasets to extract valuable insights that drive decision-making. They employ machine learning algorithms, statistical models, and advanced programming to make predictions, classify data, and identify trends. Key skills include proficiency in programming languages like Python and R, data manipulation using SQL, and machine learning frameworks such as TensorFlow and scikit-learn. Data scientists work closely with business leaders to understand their goals and develop data-driven strategies that improve operations. They find employment across various sectors, including healthcare, finance, retail, and technology, where they leverage their expertise to solve complex business challenges and foster innovation.
2. Data Analyst
Data analysts focus on transforming raw data into meaningful insights by using statistical tools and visualizations. Unlike data scientists, their primary task is to interpret historical data and present it in an accessible format for decision-making. They typically work with tools like Excel, Tableau, SQL, and Power BI to clean, process, and analyze data, creating reports and dashboards for organizational use. Data analysts also monitor trends and patterns in data, helping businesses improve their operations and optimize performance. While data scientists build predictive models, analysts focus more on explaining past trends and providing actionable insights for short-term strategies. Industries such as retail, marketing, finance, and healthcare actively seek skilled data analysts.
3. Machine Learning Engineer
Machine learning engineers design, implement, and optimize machine learning models that automate decision-making processes. They work with large datasets and ensure algorithms run efficiently in real-world applications. This role requires deep technical knowledge, including proficiency in Python, C++, or Java, along with machine learning frameworks such as TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Keras. ML engineers are responsible for selecting the right models, tuning hyperparameters, and ensuring scalability, which makes them essential in building systems for prediction, recommendation, and classification tasks. ML engineers are employed by companies in sectors like technology, finance, healthcare, and automotive, where automation and intelligent systems are key to their operations.
4. Data Engineer
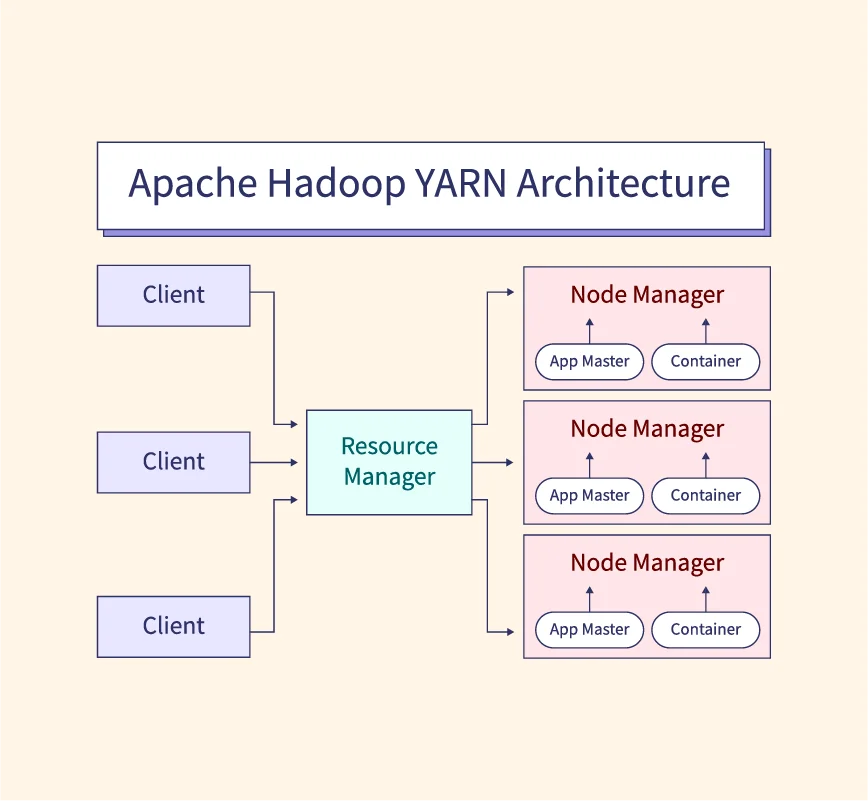
Data engineers are key to building and managing robust data systems that handle the flow, storage, and transformation of data. They design and implement data pipelines, ensuring data is clean, structured, and accessible for analysis. Their primary responsibilities include managing databases, optimizing data storage solutions, and integrating various data sources for seamless data flow. Using technologies like Hadoop, Apache Spark, and AWS, they ensure that data systems are scalable and efficient. Unlike data scientists, who analyze data, data engineers focus on the infrastructure required to support data science work. They often collaborate with data scientists to ensure data accessibility and usability.
5. Business Intelligence (BI) Analyst
Business Intelligence (BI) analysts play a crucial role in helping organizations derive valuable insights from data. They use tools such as Power BI, Tableau, and Google Analytics to create visualizations, reports, and dashboards that make data accessible for decision-makers. BI analysts are skilled in interpreting historical data, identifying trends, and providing actionable recommendations to improve business performance. Their work enables organizations to track key performance indicators (KPIs), optimize strategies, and enhance operational efficiency. BI analysts commonly work in industries such as finance, healthcare, and retail, ensuring that business leaders have accurate, timely data to inform decisions.
6. Data Architect
Data architects are responsible for designing and building the infrastructure required to store and manage an organization’s data. They focus on structuring databases, creating data models, and ensuring that data storage solutions are scalable and secure. Data architects use SQL, NoSQL, and various cloud technologies to design systems that support data analysis and business needs. They collaborate with data engineers and data scientists to ensure that the data infrastructure is optimized for analysis and reporting. Data architects typically work in industries like technology, healthcare, and finance, ensuring that data is structured efficiently for analysis and decision-making.
7. Data Science Manager/Director
Data Science Managers and Directors oversee data science teams and projects, ensuring alignment with organizational goals. They provide leadership, guidance, and strategic direction for data-driven initiatives. These professionals manage team workflows, set priorities, and ensure that data science projects are completed on time and within scope. Transitioning from technical roles, they must have a deep understanding of data science methodologies, but their focus shifts toward leadership and strategy. They frequently work with senior management and stakeholders to translate business requirements into actionable data solutions. Career growth for data science managers includes advancing to executive-level positions or specialized data leadership roles.
8. Data Science Consultant
Data Science Consultants offer specialized expertise to organizations, advising on data-driven strategies and solutions. These professionals analyze business problems and identify opportunities for improvement through data insights. They help organizations leverage advanced data techniques, such as machine learning, predictive analytics, and statistical modeling, to make informed decisions. Data science consultants can work independently as freelancers or within consulting firms. They often collaborate with businesses across various industries, including finance, healthcare, and e-commerce. Consultants must have strong technical skills and the ability to communicate complex findings in a way that is accessible to non-technical stakeholders.
9. Data Science Product Manager
A Data Science Product Manager bridges the gap between data science teams and business stakeholders. They focus on defining and overseeing the development of data-centric products and solutions, ensuring that products meet user needs while aligning with business objectives. These professionals work closely with data scientists, engineers, and designers to prioritize features, manage product lifecycles, and ensure seamless integration of machine learning models and data pipelines. Key skills for this role include project management, communication, and a deep understanding of AI and machine learning. Many tech companies hire data science product managers to drive the development of innovative data products.
10. Data Science Educator/Trainer
Data Science Educators or Trainers teach data science concepts at universities, boot camps, and online platforms. They guide students through the foundations of data analysis, machine learning, and statistical modeling, ensuring that future professionals are well-equipped to tackle real-world problems. Trainers often develop curricula, teach courses, and evaluate student progress. With the rise of online education, demand for data science instructors is increasing. Becoming a data science educator requires a strong background in the field, along with effective teaching and communication skills. Universities, private institutions, and e-learning platforms frequently hire qualified data science educators.
11. Data Science Researcher
Data Science Researchers focus on advancing the field by developing new algorithms, models, and techniques in data analysis. They work in academia, research institutions, or corporate R&D departments, aiming to push the boundaries of artificial intelligence and machine learning. Their work often involves publishing papers, collaborating with other researchers, and contributing to open-source projects. Data science researchers are typically experts in areas such as deep learning, natural language processing, and computer vision. This role requires a high level of technical expertise, creativity, and a passion for discovery. Many data science researchers have PhDs in relevant fields.
12. Data Science Entrepreneur
Data Science Entrepreneurs build and scale companies that leverage AI, machine learning, and data analytics to solve business problems. They create startups or innovations that apply data-driven insights in sectors like healthcare, finance, retail, and more. A data science entrepreneur needs to combine technical expertise with business acumen, as they are responsible for both developing products and securing investments. Challenges include staying ahead of technological trends, acquiring data, and managing talent. However, the opportunities in this rapidly growing field are immense, with data science becoming integral to industries worldwide. Successful data science entrepreneurs often pioneer new business models.
How Different Data Science Roles Work Together in a Project
In a data science project, collaboration between various roles is essential for success. Data scientists, engineers, analysts, and managers form a cross-functional team, each contributing their expertise to deliver solutions. The data engineer builds and maintains the infrastructure, ensuring data is clean and accessible. Data scientists apply machine learning algorithms and statistical models to uncover insights. Data analysts focus on visualizing the results and communicating findings to stakeholders. Meanwhile, data science managers oversee the project, ensuring alignment with business goals and managing team dynamics.
For example, in a customer segmentation project, the data engineer would prepare and structure customer data, while the data scientist would create clustering models to group customers based on behavior. The data analyst would then visualize these clusters and present actionable insights, such as personalized marketing strategies. The manager would ensure the project meets deadlines and aligns with business objectives.
This seamless collaboration is crucial to extracting value from data and driving business decisions. Teams with a mix of technical and business-focused professionals tend to deliver the most successful data science projects.
Career Opportunities and Growth in Data Science
Data science continues to be one of the most in-demand fields globally, offering numerous career opportunities across various industries. With the exponential growth of data, organizations are actively seeking professionals with the ability to extract valuable insights and develop data-driven solutions. Job roles in data science, such as data scientists, analysts, engineers, and machine learning experts, are thriving, and companies in sectors like healthcare, finance, e-commerce, and technology are hiring extensively.
The salary prospects in data science are highly attractive, with many roles offering competitive compensation packages. As businesses increasingly rely on data, the demand for skilled professionals is expected to grow, creating long-term career stability. Additionally, advancements in AI, machine learning, and automation open new avenues for career growth.
Future trends in data science careers include a focus on specialized skills, such as deep learning and reinforcement learning, along with an increased emphasis on data ethics and privacy. Aspiring data scientists should continuously learn and adapt to stay ahead in this rapidly evolving field.
Conclusion
Data science roles are essential in driving business transformation and innovation across industries. With a wide range of career paths available, there is ample opportunity for professionals to specialize and grow. As the demand for data-driven decision-making continues to increase, the future of data science careers looks promising. For those looking to enter the field, it’s essential to understand the diverse roles and their impact. Embracing data science offers both rewarding opportunities and the chance to shape the future.
References –