In the era of information, where terabytes of data are generated every second, the ability to extract meaningful insights from this deluge is a prized skill. Data Science, the multidisciplinary field that combines scientific methods, processes, algorithms, and systems to extract knowledge and insights from structured and unstructured data, is at the forefront of this revolution. A report by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts a staggering 36% growth in data science and analytics jobs between 2021 and 2031, underscoring the surging demand for skilled data professionals.
From healthcare and finance to marketing and manufacturing, Data Science has infiltrated every industry, transforming the way we operate and make decisions. This guide will delve into the world of Data Science, exploring its significance, career paths, applications, and the steps to get started in this dynamic field.
What is Data Science?
Data Science is a field that involves collecting, analyzing, and interpreting large amounts of data to help solve problems and make informed decisions. It’s like finding patterns in huge piles of information. Imagine having a giant puzzle, and each piece of data helps you see the bigger picture. Data Science is used in various fields, such as business, healthcare, and technology, to understand trends, make predictions, and improve processes.
The History and Evolution of Data Science
The roots of data science can be traced back to the early days of statistics and computer science. However, it wasn’t until the rise of big data and advanced computing power that the field truly took off.
Key milestones in the development of data science include the invention of the relational database, the development of statistical software, and the emergence of machine learning algorithms.
Why is Data Science Important?
1. Decision Making: Businesses and organizations use data to make better decisions. For example, companies analyze customer data to understand what products people like and then create more of those products.
2. Predicting the Future: Data Science can help predict future trends. For instance, weather forecasting uses data from satellites, sensors, and other sources to predict the weather days in advance.
3. Solving Problems: Data Science can identify problems that are not obvious. In healthcare, data can reveal patterns in patient symptoms that help doctors diagnose diseases more accurately.
Key Concepts in Data Science
1. Data Collection: This is the process of gathering information. Data can come from various sources like surveys, sensors, websites, and social media.
2. Data Cleaning: Not all data is useful. Data cleaning involves removing or fixing incorrect, incomplete, or irrelevant data to make sure the analysis is accurate.
3. Data Analysis: Once the data is clean, it’s time to analyze it. Data analysis involves looking for patterns, trends, or relationships in the data. For example, a company might analyze sales data to find out why a particular product is selling well.
4. Data Visualization: Data visualization is the process of turning data into visual formats like charts, graphs, or maps. This makes it easier to understand and communicate the findings to others.
5. Machine Learning: Machine learning is a type of artificial intelligence (AI) where computers learn from data to make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed. For example, Netflix uses machine learning to recommend movies based on your watching history.
Applications of Data Science
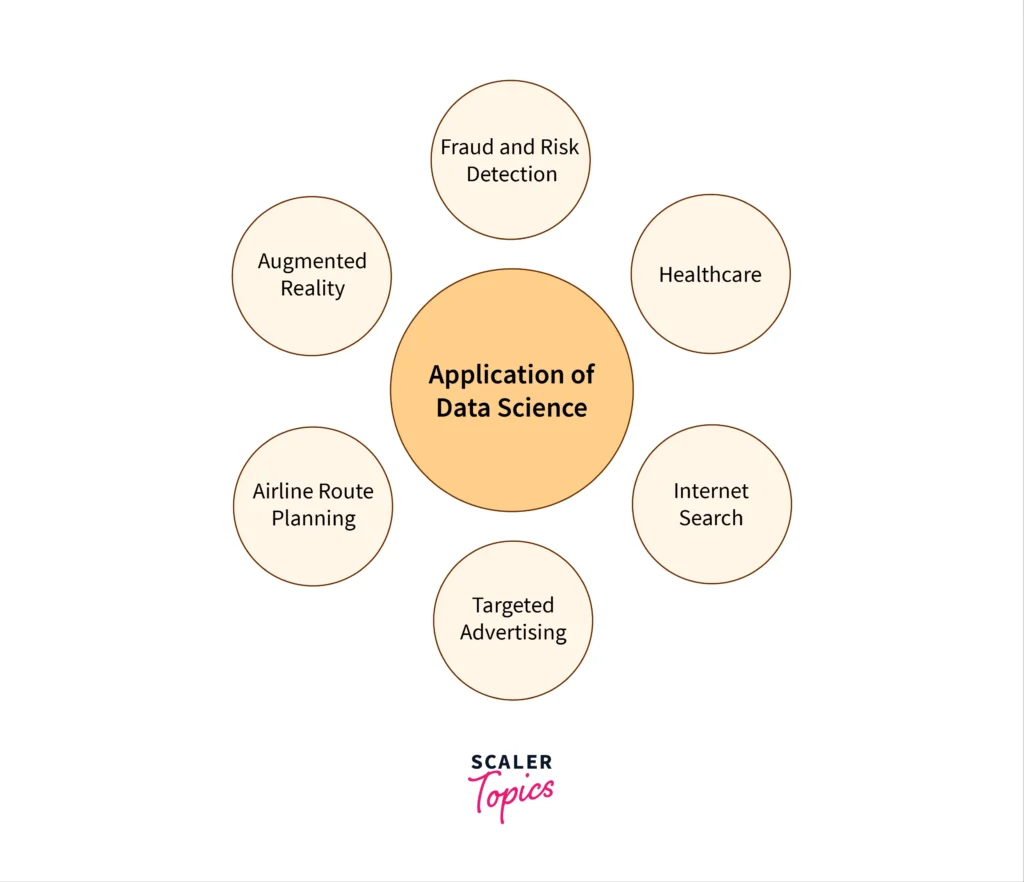
1. Business: Companies use data science to improve their operations, target marketing efforts, and increase sales. For instance, Amazon uses data science to recommend products to customers based on their browsing and purchase history.
2. Healthcare: In healthcare, data science helps in diagnosing diseases, discovering new treatments, and improving patient care. For example, by analyzing patient data, doctors can predict who is at risk of developing certain conditions.
3. Finance: Financial institutions use data science to detect fraud, manage risks, and automate trading. For instance, credit card companies use data science to identify unusual spending patterns that might indicate fraud.
4. Social Media: Platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram use data science to personalize content for users, detect fake accounts, and show relevant advertisements.
5. Transportation: Data science is used in transportation to optimize routes, reduce traffic congestion, and improve public transport systems. For example, ride-sharing apps like Uber use data science to match drivers with passengers efficiently.
Getting Started with Data Science
1. Learn the Basics: Start by learning basic concepts like statistics, probability, and basic programming. Python is a popular language for data science due to its simplicity and vast libraries.
2. Practice with Real Data: The best way to learn data science is by working on real data. You can find datasets online to practice analyzing and visualizing data.
3. Explore Tools and Technologies: Familiarize yourself with tools like Excel, SQL, and Python libraries like Pandas, NumPy, and Matplotlib. These are commonly used in data science projects.
4. Join a Community: Joining a community of data science enthusiasts can help you stay motivated and learn from others. Websites like Kaggle offer competitions and projects to work on real-world data problems.
Careers in Data Science
- Data Scientist: Extracts insights from data, builds predictive models, and communicates findings to stakeholders.
- Data Analyst: Cleans, transforms, and analyzes data to answer business questions and support decision-making.
- Data Engineer: Designs, builds, and maintains the infrastructure and pipelines for data collection, storage, and processing.
- Machine Learning Engineer: Develops and deploys machine learning models to solve complex problems and automate tasks.
- Business Intelligence Analyst: Uses data to identify trends and opportunities, create visualizations, and generate reports for business insights.
- Data Architect: Designs and implements the overall data architecture and strategy for an organization.
- Statistician: Applies statistical methods to analyze data, design experiments, and draw conclusions.
The field of Data Science offers a diverse range of career paths, catering to various skill sets and interests. Whether you’re passionate about uncovering insights, building models, or designing data infrastructure, there’s a role that aligns with your aspirations. From entry-level positions like Data Analysts to specialized roles like Machine Learning Engineers, the career opportunities in Data Science are vast and ever-evolving.
The Future of Data Science
The future of data science is bright. Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are set to revolutionize the field. AI-powered tools can automate repetitive tasks, enabling data scientists to focus on higher-level analysis and problem-solving.
As data continues to grow in volume and complexity, data science will play an even more critical role in unlocking its full potential.
Prerequisites and Tools for Data Science
- Programming: Proficiency in Python or R.
- Statistics: Understanding of statistical concepts and methods.
- Mathematics: Linear algebra and calculus fundamentals.
- Data Visualization: Experience with tools like Matplotlib, PowerBI, Quilsense, Quilview, Seaborn, or Tableau.
- Machine Learning: Familiarity with algorithms and techniques.
- Database Management: Basic SQL knowledge.
- Tools: Jupyter Notebooks, Pandas, NumPy, Scikit-learn, TensorFlow, Keras.
Conclusion
Data Science is a powerful tool that can help solve complex problems, make informed decisions, and predict future trends. Whether you’re a beginner or an expert, understanding the basics of data science can open up many opportunities in various fields.
Additional Resources on Data Science
1. Introduction and Basics of Data Science
These blogs explain what data science is, its differences from related fields, and its importance.
- What is Data in Data Science?
- Data Science vs Data Analytics
- Data Science and Machine Learning: What’s the Difference?
- Data Science vs Computer Science
- Components of Data Science
- Data Science Project
- What is Data Processing
- Exploratory Data Analysis
- What is Data Modeling
2. Learning Pathways and Career Guidance
These blogs cover the roadmap, necessary skills, and career-related advice for aspiring data scientists.
- How to Become a Data Scientist
- Data Science Roadmap
- Is Data Science a Good Career?
- Top Data Scientist Skills
- Soft Skills for Data Scientists
- Data Scientist vs Data Engineer
- Data Science Interview Questions
- How to Become a Data Scientist After 12th
- How to Become a Data Scientist in India
- How to Learn Data Science
- Data Science and Computer Science
- Data Science Books
3. Data Science Courses, Tools, and Resources
These blogs focus on courses, learning resources, and tools used in data science.
- Data Science Course Syllabus and Subjects
- Python Libraries for Data Science
- Data Science Tools
- Python vs R for Data Science
- Why Use Python for Data Science?
- What is R in Data Science?
- Best Python Books for Data Science
- How to Learn Python for Data Science
4. Data Preparation and Analysis Techniques
These blogs focus on the data preparation steps and key analytical techniques involved in data science.
- What is Data Preparation?
- Exploratory Data Analysis
- Data Science Process
- Data Science Lifecycle
- Data Preprocessing in Data Science
- Data Cleaning in Data Science
- What is Data Wrangling?
- What is Data Collection?
- ETL in Data Science
- Data Aggregation
- Inferential Statistics
- Descriptive Statistics
- Covariance and Correlation
5. Mathematics and Statistics for Data Science
These blogs cover the mathematical and statistical foundations necessary for data science.
6. Applications and Industry Use Cases
These blogs highlight how data science is applied across industries and its impact.
7. Challenges and Future Scope
These blogs discuss the challenges faced by data scientists and the future of the field.